[Windows Migration] Migrating SQL Server to openEuler
Overview
Many enterprises and individuals have switched from Windows to Linux in recent years, and more are following suit. Linux has long dominated the network server market with its superior stability, reliability, cost-efficiency, and security. It can handle challenging workloads with high availability and high performance, offer a better user experience, and provide a diverse tool set. These are the reasons why people prefer Linux.
Microsoft rebuilt SQL Server in 2016 to make most of its functions OS-independent. This project enables more users to move their application services from the Windows platform to the Linux platform. This blog describes how to migrate SQL Server 2019 to openEuler to help users migrate data on the Windows platform.
Installing SQL Server and Creating a Database on openEuler
Preparations
For details, see https://www.cnblogs.com/linuxjava/p/17456089.html.
Installing Python 2
Installing SQL Server 2019 requires Python 2 dependencies. However, Python 2 is not provided in the default Yum source. Therefore, you need to manually download and install Python 2.
- Use wget to obtain the Python package.
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.7.9/Python-2.7.9.tgz- Install the basic libraries required by Python 2.
sudo yum install zlib-devel bzip2-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel gcc make libffi-devel- If tar is not installed, install it first.
sudo yum install tar -y- Decompress and install Python 2.
# Run the tar command to decompress the package.
tar xzf Python-2.7.9.tgz
# Go to the extracted directory.
cd Python-2.7.9
# Generate MakeFile.
sudo ./configure --prefix=/usr/local
# Install Python 2.
sudo make altinstall- Create a soft link for the Python software in the
/usr/local/bin/directory to the/usr/bin/directory.
sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/python2.7 /usr/bin/python
sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/python2.7 /usr/bin/python2Creating a Soft Link for the .so File
The liblber-2.4.so.2 and libldap-2.4.so.2 files do not exist in the system, but the liblber.so.2 and libldap.so.2 files exist (the file names do not contain the version number). You can create a soft link to replace them.
sudo ln -s /usr/lib64/liblber.so.2 /usr/lib64/liblber-2.4.so.2
sudo ln -s /usr/lib64/liblber.so.2 /usr/lib/liblber-2.4.so.2
sudo ln -s /usr/lib64/libldap.so.2 /usr/lib/libldap-2.4.so.2
sudo ln -s /usr/lib64/libldap.so.2 /usr/lib64/libldap-2.4.so.2Installing SQL Server
For details, see https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/linux/quickstart-install-connect-red-hat?view=sql-server-ver15&tabs=rhel8.
Installing the SQL Server Service
- openEuler does not have an SQL Server source and is similar to Red Hat. Therefore, the Red Hat repository is used as the download source. Download the SQL Server 2019 (15.x) Red Hat repository configuration file.
sudo curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/mssql-server.repo https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/8/mssql-server-2019.repo- Install SQL Server.
sudo yum install -y mssql-server- Run mssql-conf setup, set the SA password as prompted, and select a version. Evaluation, Developer, and Express editions are free of charge.
sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf setupComplete the settings as prompted. 4. After the configuration is complete, check whether the service is running.
systemctl status mssql-server- Enable the SQL Server port on the firewall. The default SQL Server port is TCP 1433.
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=1433/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadFor firewalls other than FirewallD, run the corresponding command.
Disabling the sa Account
According to the official document, the sa account must be disabled after the installation to ensure security. However, the sa account will be used in this tutorial. Therefore, skip this step. You can determine whether to disable the sa account based on security requirements.
For details, see https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/linux/quickstart-install-connect-red-hat?view=sql-server-ver15&tabs=rhel8#disable-the-sa-account-as-a-best-practice.
Installing the SQL Server Command Line Tool
- In this step, you need to use the Red Hat repository as the download source again. Download the Microsoft Red Hat repository configuration file.
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/8/prod.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mssql-release.repo- If an earlier version of mssql-tools is installed, delete all old unixODBC packages.
sudo yum remove mssql-tools unixODBC-utf16 unixODBC-utf16-devel- Install mssql-tools18 using the unixODBC developer package.
sudo yum install -y mssql-tools18 unixODBC-devel- Update mssql-tools to the latest version.
sudo yum check-update
sudo yum update mssql-tools18- Add
/opt/mssql-tools18/bin/to thePATHenvironment variable in the bash shell: To make sqlcmd and bcp accessible from the bash shell of the login session, run the following command to modifyPATHin the~/.bash_profilefile:
echo 'export PATH="$PATH:/opt/mssql-tools18/bin"' >> ~/.bash_profileTo make sqlcmd and bcp accessible from the bash shell of interactive/non-login sessions, run the following command to modify PATH in the ~/.bashrc file:
echo 'export PATH="$PATH:/opt/mssql-tools18/bin"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrcConnecting to the Database
Run sqlcmd with parameters for the SQL Server name (-S), the user name (-U), and the password (-P).
sqlcmd -S localhost -U sa -P '<YourPassword>'In the preceding command, the connection is made locally, the server name is localhost, the user name is sa, and the password is the one specified for sa during setup.
If you do not want to enter the password in explicit mode, you can omit the -P option and the corresponding parameter. After the command is executed, the system prompts you to enter the password.
If an SSL certificate authentication failure error occurs during login, add the -C option to solve the problem.
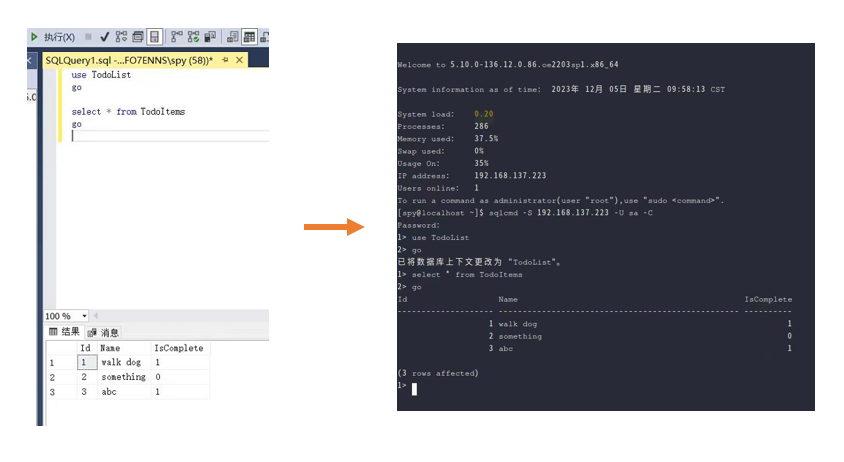
When the sqlcmd command prompt 1> is displayed, the connection is successful.
For example, the following is a successful interaction case.
[spy@localhost ~]$ sqlcmd -S 192.168.137.223 -U sa -C
Password: # Enter the password. The password is not displayed.
1> # The login is successful. You can enter SQL statements.In the preceding example, 192.168.137.223 is the local IP address. You can replace it with the remote IP address if needed.
To exit sqlcmd, enter exit or quit.
Migrating SQL Server Data to openEuler
For details, see https://learn.microsoft.com/en-gb/sql/linux/sql-server-linux-migrate-restore-database?view=sql-server-ver15.
Replace YourDB with the actual database name.
Backing Up Data
In the Microsoft official document, SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is used to create backup files in graphical interaction mode. Due to the diversity of database management systems, this method is not applicable if other database management systems are used or the graphical management system is not used. Therefore, this method is not described here. If you want to use this method, see https://learn.microsoft.com/en-gb/sql/linux/sql-server-linux-migrate-restore-database?view=sql-server-ver15#create-a-backup-on-windows.
You are advised to use SQL statements that are easy to operate and widely applicable.
BACKUP DATABASE [YourDB] TO DISK = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Backup\YourDB.bak'
WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT, NAME = N'YourDB-Full Database Backup',
SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10
GOIf user permission problems occur, perform the following operations:
Open the Windows service (press Win+R and enter services.msc or use other methods to open the service), find the corresponding database instance service (for example, SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER), right-click the service, choose Properties from the shortcut menu, and click the Login tab, change the login user to a local system account or assign required permissions to a specified account.
After the backup file is generated, use the scp command to transfer the file to openEuler.
Migrating Data
- Enter the super user mode.
sudo su- Create a backup directory.
mkdir -p /var/opt/mssql/backup- Move the backup file to the directory. (Assume that the backup file is in the current directory. Change the file path or run the cd command to go to the correct directory.)
mv YourDB.bak /var/opt/mssql/backup/The purpose of moving the backup file is as follows: The subdirectory of /var/opt/mssql belongs to user mssql and group mssql. 4. Exit the super user mode.
exit- Start sqlcmd.
sqlcmd -S 192.168.137.223 -U sa -C- Log in to sqlcmd and enter the following SQL statements:
RESTORE DATABASE YourDB
FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/backup/YourDB.bak'
WITH MOVE 'YourDB' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB.mdf',
MOVE 'YourDB_Log' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB_Log.ldf'
GOMultiple lines of commands cannot be copied and pasted at the same time in sqlcmd.
If the operation is successful, you should receive a message indicating that the database is successfully restored.
If an error similar to the following occurs:
File 'YourDB_Product' cannot be restored to 'Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Product.ndf'. Use WITH MOVE to identify a valid location for the file.
Msg 5133, Level 16, State 1, Server servername, Line 1
Directory lookup for the file "Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Product.ndf" failed with the operating system error 2(The system cannot find the file specified.).In this case, the database contains secondary files. If these files are not specified in the MOVE clause of RESTORE DATABASE, the restore procedure will try to create them in the same path as the original server.
You can list all the files contained in the backup.
RESTORE FILELISTONLY FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/backup/YourDB.bak'
GOYou should see the following list (only the first two columns are listed):
LogicalName PhysicalName ..............
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
YourDB Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB.mdf ..............
YourDB_Product Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Product.ndf ..............
YourDB_Customer Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Customer.ndf ..............
YourDB_log Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Log.ldf ..............You can use this list to create MOVE clauses for other files. In this example, RESTORE DATABASE is:
RESTORE DATABASE YourDB
FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/backup/YourDB.bak'
WITH MOVE 'YourDB' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB.mdf',
MOVE 'YourDB_Product' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB_Product.ndf',
MOVE 'YourDB_Customer' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB_Customer.ndf',
MOVE 'YourDB_Log' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB_Log.ldf'
GO- Check whether the restoration is successful by listing all databases.
SELECT Name FROM sys.Databases
GO- Data migration is successful.
The Porting Platform WinApp SIG demonstrates the SQL Server migration solution described in this document. If you are interested in Windows migration technologies, you are welcome to join us by scanning the following QR code to join the SIG WeChat group.

